Mouse breeding is the backbone of in vivo biomedical research, supporting immunology, cancer biology, genetic engineering, and cell therapy development.
𝗕𝗿𝗲𝗲𝗱𝗶𝗻𝗴 𝗕𝗮𝘀𝗶𝗰𝘀
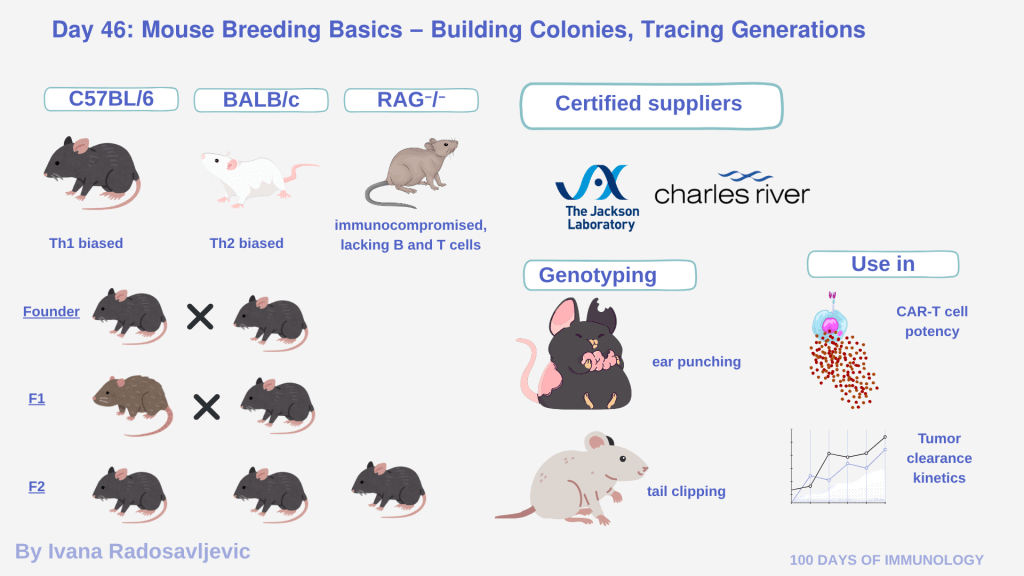
Common laboratory strains include C57BL/6 (B6), BALB/c, and RAG-knockout (RAG⁻/⁻) mice. Each strain carries unique immunological traits: C57BL/6 mice are robust and Th1-biased, BALB/c favor Th2-type responses, and RAG-deficient mice lack functional B and T cells, making them ideal for xenograft studies [1].
Breeding schemes typically begin with founder pairs, where genetic traits are stabilized across F1, F2, and subsequent generations. Maintaining colonies has to plan to avoid inbreeding depression and genetic drift. Institutions often rely on The Jackson Laboratory (JAX) and Charles River Laboratories, two of the largest global providers of genetically defined mouse models [2][3].
𝗚𝗲𝗻𝗼𝘁𝘆𝗽𝗶𝗻𝗴 𝗮𝗻𝗱 𝗜𝗱𝗲𝗻𝘁𝗶𝗳𝗶𝗰𝗮𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻
To confirm genotypes, small tissue samples are collected.
𝘌𝘢𝘳 𝘱𝘶𝘯𝘤𝘩𝘦𝘴 are a permanent identification mark and a source of DNA for PCR genotyping.
𝘛𝘢𝘪𝘭 𝘣𝘪𝘰𝘱𝘴𝘪𝘦𝘴, taken from 2–3 mm of the distal tail tip in young pups, provide high-quality DNA [4]. DNA is extracted from these samples, and specific genetic markers are amplified using PCR to verify the presence or absence of the target allele.
𝗫𝗲𝗻𝗼𝗴𝗿𝗮𝗳𝘁 𝗮𝗻𝗱 𝗦𝘆𝗻𝗴𝗲𝗻𝗲𝗶𝗰 𝗠𝗼𝗱𝗲𝗹𝘀
𝘚𝘺𝘯𝘨𝘦𝘯𝘦𝘪𝘤 𝘮𝘰𝘥𝘦𝘭𝘴 use tumor cells derived from the same genetic background as the host, preserving an intact immune system — ideal for immune-oncology testing [5].
𝘟𝘦𝘯𝘰𝘨𝘳𝘢𝘧𝘵 𝘮𝘰𝘥𝘦𝘭𝘴, involve implanting human tumor or immune cells into immunocompromised mice (such as NSG, NOD-SCID, or RAG⁻/⁻ strains). Allow human-derived CAR-T, CAR-M, or immune checkpoint studies to proceed without host immune rejection [6].
𝘏𝘶𝘮𝘢𝘯𝘪𝘻𝘦𝘥 𝘮𝘪𝘤𝘦, generated through hematopoietic stem cell or PBMC engraftment, provide even closer representation of human immune responses.
Such model systems are invaluable for evaluating CAR-T potency, tumor clearance kinetics, and cytokine release profiles before clinical translation.
𝗤𝘂𝗲𝘀𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻 𝗳𝗼𝗿 𝗿𝗲𝗮𝗱𝗲𝗿𝘀: Do you rely on in-house breeding or external certified providers?
Stay tuned for 𝗗𝗮𝘆 𝟰𝟳: 𝗗𝗿𝘂𝗴 𝗗𝗼𝘀𝗶𝗻𝗴 𝗳𝗼𝗿 𝗠𝗶𝗰𝗲 – 𝗖𝗮𝗹𝗰𝘂𝗹𝗮𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻𝘀 𝗮𝗻𝗱 𝗣𝗿𝗮𝗰𝘁𝗶𝗰𝗮𝗹 𝗖𝗼𝗻𝘀𝗶𝗱𝗲𝗿𝗮𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻𝘀
𝗥𝗲𝗳𝗲𝗿𝗲𝗻𝗰𝗲𝘀
1. DOI:10.1038/nri2017
2. https://www.jax.org/
3. https://www.criver.com/
4. DOI: 10.17226/12910
5. DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abm8564
6. https://lnkd.in/em_fHZ8f
hashtag#MouseBreeding hashtag#InVivoResearch hashtag#Immunology hashtag#XenograftModel hashtag#SyngeneicModel hashtag#CARResearch hashtag#AnimalModels hashtag#LabLife hashtag#ResearchEthics hashtag#100DaysOfImmunology