Laboratory automation is growing in immunology research, biotechnology, and clinical manufacturing. Automation means the use of programmable, standardized systems that execute experimental workflows with minimal human intervention, ensuring consistency, accuracy, reproducibility, and high throughput. [2]
𝗔𝘂𝘁𝗼𝗺𝗮𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻 𝗧𝗼𝗼𝗹𝘀
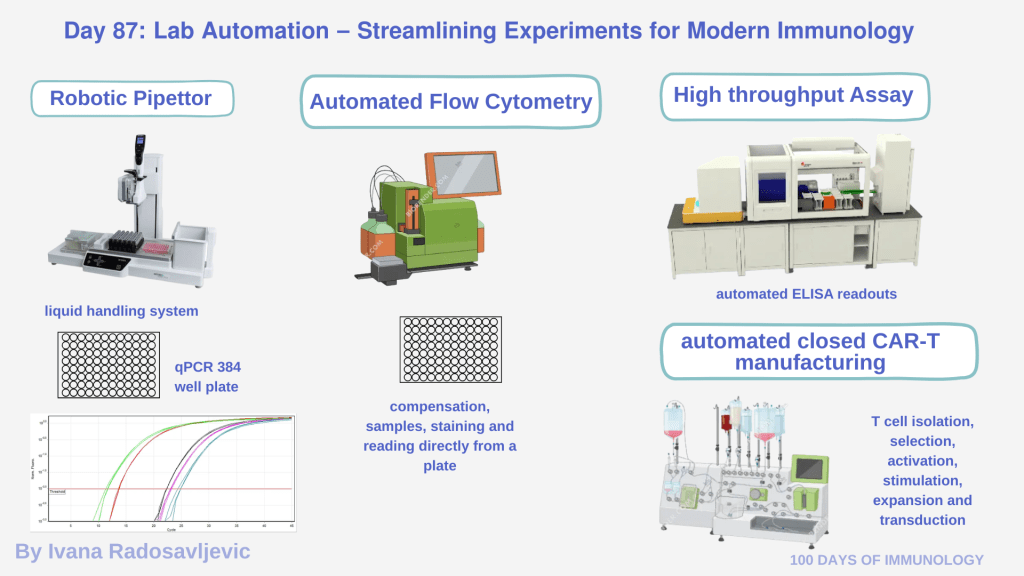
𝗥𝗼𝗯𝗼𝘁𝗶𝗰 𝗣𝗶𝗽𝗲𝘁𝘁𝗶𝗻𝗴 Platforms
Robotic pipettors – Integra Voyage or Tecan systems enable precise, large-scale liquid handling. They significantly reduce manual error and biological variability.
In academia, I had the opportunity to work with a robotic pipettor for qPCR in 384-well plates. Running four plates per day manually would require hours of pipetting and risk of repetitive strain injuries (experienced mild in current role). The robot reduced this to minutes, allowing me to focus on assay design and data interpretation.
This would not have been achievable without the support of a highly skilled and creative research technician, A.
𝗔𝘂𝘁𝗼𝗺𝗮𝘁𝗲𝗱 𝗙𝗹𝗼𝘄 𝗖𝘆𝘁𝗼𝗺𝗲𝘁𝗿𝘆
Instruments such as the MACSQuant Analyzer provide automated compensation, multi-parameter acquisition, and direct sample loading from plates. For studies involving hundreds or thousands of samples like immunoprofiling in clinical cohort, automation enables reliable high-dimensional data at unprecedented speed.
𝗛𝗶𝗴𝗵-Throughput 𝗔𝘀𝘀𝗮𝘆 𝗣𝗹𝗮𝘁𝗳𝗼𝗿𝗺𝘀
Automation makes the following routine:
• High-throughput ELISA kits with robotic plate washers and readers
• Automated fluorescence detection for multiplex cytokine panels
• Microfluidics and droplet platforms for screening millions of cells simultaneously
𝗔𝘂𝘁𝗼𝗺𝗮𝘁𝗲𝗱, 𝗖𝗹𝗼𝘀𝗲𝗱 𝗖𝗔𝗥-𝗧 Manufatcuring
If we can fully automate cell isolation, activation, transduction, expansion, and formulation in a closed system for CAR-T products [1], the same principles can (and should) be adapted for academic research.
Automating workflows reduces contamination risks, increases experiment throughput, and ensures process reproducibility essential for preclinical immunotherapy design.
Researchers like Nikolay Dobrev a strong advocate for laboratory automation, emphasize the value of integrating robotics to accelerate discovery.
𝗤𝘂𝗲𝘀𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻 𝗳𝗼𝗿 𝘁𝗵𝗲 𝗔𝘂𝗱𝗶𝗲𝗻𝗰𝗲
If you could automate one part of your lab workflow tomorrow—just one—what would it be?
Stay tuned for 𝗗𝗮𝘆 88: 𝟯𝗗 𝗣𝗿𝗶𝗻𝘁𝗶𝗻𝗴 𝗶𝗻 𝗯𝗶𝗼𝗺𝗲𝗱𝗶𝗰𝗮𝗹 𝗿𝗲𝘀𝗲𝗮𝗿𝗰𝗵
𝗥𝗲𝗳𝗲𝗿𝗲𝗻𝗰𝗲𝘀
1. DOI: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2016.36
2. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0020124
#LabAutomation #Immunology #HighThroughput #FlowCytometry #qPCR #BiotechInnovation #CAR-T #ResearchWorkflows #AutomationInScience #100DaysofImmunology